In this post, we will see comparison between Spring Boot and LoopBack – Node.js for implementing Microservices.
SpringBoot
Spring Boot is an open source Java-based framework used to create Microservices. It is developed by Pivotal Team and is used to build stand-alone and production ready spring applications.
Microservices architecture using Java Spring Boot
LoopBack – Node.js
Events and event-driven programming
Events are actions generated by the user or the system, like a click, a completed file download, or a hardware or software error.
Event-driven programming is a programming paradigm in which the flow of the program is determined by events. An event-driven program performs actions in response to events. When an event occurs it triggers a callback function.
Node.js is a platform that executes server-side JavaScript programs that can communicate with I/O sources like file systems and networks.
LoopBack
LoopBack is a highly extensible, open-source Node.js and TypeScript framework based on Express that enables you to quickly create APIs and microservices composed from backend systems such as databases and SOAP or REST services.
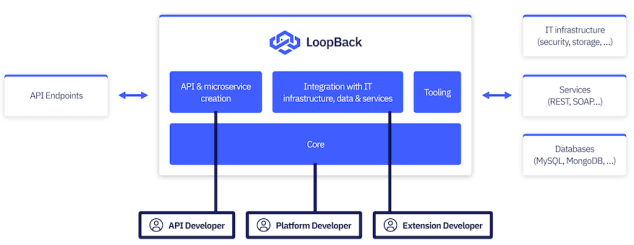
The diagram below demonstrates how LoopBack serves as a composition bridge between incoming requests and outgoing integrations. It also shows the different personas who are interested in various capabilities provided by LoopBack.
Advantages of LoopBack – Node.js and Spring Boot
| LoopBack – Node.js | Spring Boot |
| Lightweight, fast – loosely typed | Java is statically-typed (type safety) |
| Javascript Community: growing rapidly | Java Community: mature and thriving |
| Great for I/O tasks. Example: file writing and reading, network calls, Streaming | Long-term support and maintainability for memory intensive applications |
| Single-threaded – low memory utilization | Support for multi-threading |
| npm is constantly growing | Many easily usable dependencies using Maven, Gradle |
Disadvantages of LoopBack – Node.js and Spring Boot
LoopBack – Node.js
- Doesn’t support multi-threading
- Lack of strict type checking can lead to runtime problems
- Not great for heavy computing – performance bottlenecks
Spring Boot
- High memory utilization
- Java is verbose
- Contains lots of boilerplate code which makes debugging tough
- May include unused dependencies – huge deployment binary file size.
Industry Usage of these technologies
Companies using Spring Boot
- Amazon
- Intuit
- JP Morgan Chase & Co.
- Capital One
- Microsoft
Companies using Node.js
- FlightOffice
- Symantec
- Pen Systems
- GoDaddy.com
- Sapient
LoopBack vs SpringBoot on various parameters
| Criteria / Parameter | SpringBoot | LoopBack |
| Performance | Long-term support and maintainability for memory intensive applications | Great for I/O tasks. Example: file writing and reading, network calls, Streaming |
| Circuit Breaker | Resilience4j | Opossum |
| Hystrix | Levee | |
| Soap Client | Apache CXF, Camel, Spring WebServiceTemplate | loopback-connector-soap |
| JSON Manipulation/Validation | Jackson, Spring Validator | payload-validator |
| Orchestration and Routing support | Apache CXF, Camel, Spring WebServiceTemplate, RestTemplate | loopback-connector-soap, loopback-connector-rest |
| Caching support | Spring Cache, external cache support | Interception – CachingService, external cache support |
| Open API | Contract first, API first both are supported | Contract first, API first both are supported |
| Recommended For | Building applications which consists of Memory intensive tasks | Building applications which consists of I/O intensive tasks |
References: