This post explains how to create spring based web application.
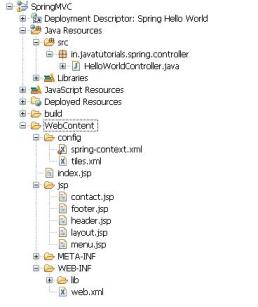
Folder Structure:
Typical folder structure of the spring web application contains as below.
web.xml:
Below is the web.xml file which contains the spring configuration. DispatcherServlet is controller of the spring mvc application, all the requests which coming to the application will be passed through it. DispatcherServlet loads the spring-context.xml file during server start up and keeps the all the configurations in servlet context. Action path configured for this applications is *.html.
<?xml version=”1.0″ encoding=”UTF-8″?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi=”http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance”
xmlns=”http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee”
xmlns:web=”http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd”
xsi:schemaLocation=”http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd”
id=”WebApp_ID” version=”2.5″><display-name>Spring Hello World</display-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>/</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list><servlet>
<servlet-name>springDispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/config/spring-context.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springDispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.html</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
index.jsp:
index.jsp file configured in web.xml as a welcome file, so this file will be loaded when user hit the http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/ url in the browser.
<jsp:forward page=”sayhello.html”></jsp:forward>
HelloWorldController.java:
When ever index.jsp loaded into the browser, it will forward the request to sayhello.html. This sayhello request is mapped to sayHello() method in HelloWorldController class. So, sayHello() method will be executed and it will return the ‘hello’ string after completion of method execution.
package in.javatutorials.spring.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;/**
*
* @author Javatutorials
*
*/
@Controller
public class HelloWorldController {/**
* Controls the ‘sayhello’ and return to hello.jsp
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value = “/sayhello”, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String sayHello() {System.out.println(“Sample Spring Application”);
return “hello”;
}}
spring-context.xml:
Package of HelloWorldController class is configured as a controller package in the spring-context file as mentioned below. This sample application is configured with the InternalResourceViewResolver, when ever sayHello() method returns the hello string, request will be redirected to hello.jsp based upon the InternalResourceViewResolver configuration as mentioned in the below file.
<?xml version=”1.0″ encoding=”UTF-8″?>
<beans xmlns=”http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans”
xmlns:xsi=”http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance” xmlns:mvc=”http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc”
xmlns:context=”http://www.springframework.org/schema/context”
xsi:schemaLocation=”
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd”><context:component-scan base-package=”in.javatutorials.spring.controller” />
<mvc:annotation-driven /><bean
class=”org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver”>
<property name=”prefix” value=”/jsp/” />
<property name=”suffix” value=”.jsp” />
</bean></beans>
hello.jsp:
Finally ‘Hi, This is Sample Spring MVC Application’ message will be shown to the user as it is mentioned in the below jsp.
<%@ page language=”java” contentType=”text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1″
pageEncoding=”ISO-8859-1″%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC “-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN” “http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd”>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv=”Content-Type” content=”text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1″>
<title>Sample Spring MVC Application</title>
</head>
<body>Hi, This is Sample Spring MVC Application
</body>
</html>
Access the application in Browser:
http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/
Please click on the below link to download the complete application : Click here
Other Useful links:
Spring MVC with Tiles framework sample application
differences between DispatchAction and LookupDispatchAction in Struts Framework